sRGB-LSMI
Revisiting Image Fusion for Multi-Illuminant White-Balance Correction, ICCV 2025
White balance (WB) correction in scenes with multiple illuminants remains a persistent challenge in computer vision. Recent methods explored fusion-based approaches, where a neural network linearly blends multiple sRGB versions of an input image, each processed with predefined WB presets. In this paper, we demonstrate that linear blending is inherently constrained, propose a new method to blend the WB presets, and introduce a new dataset: sRGB-LSMI.
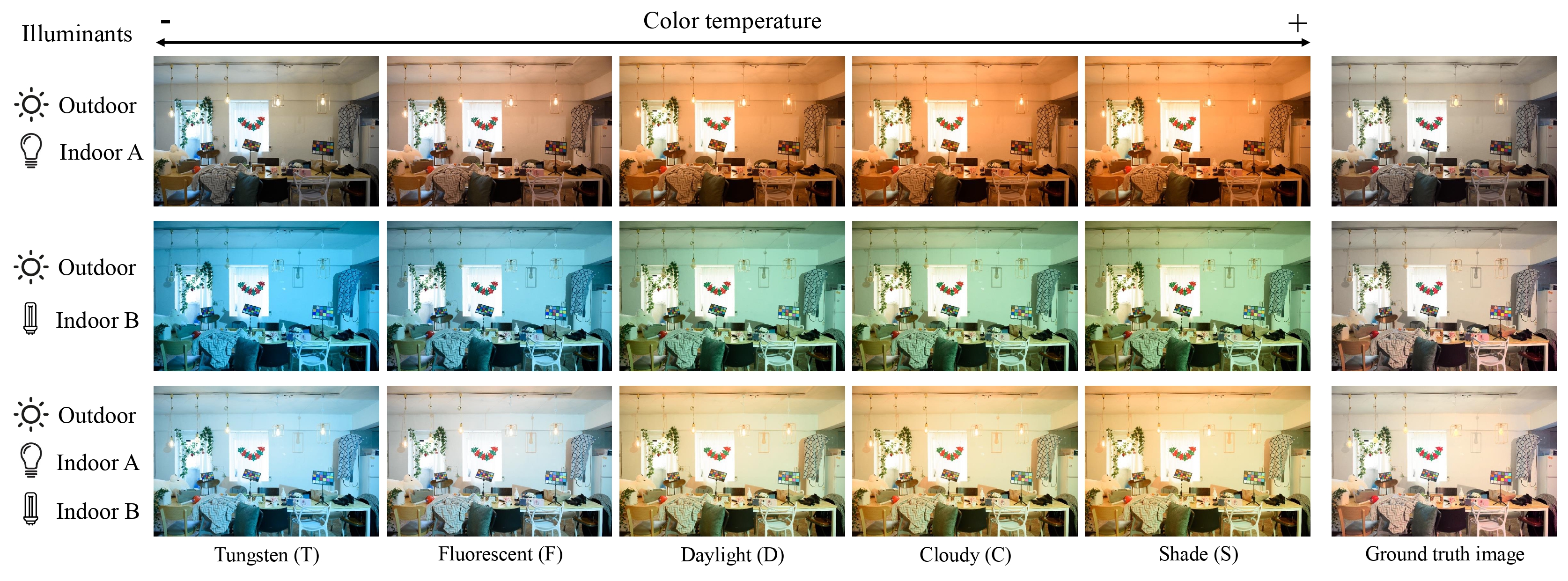

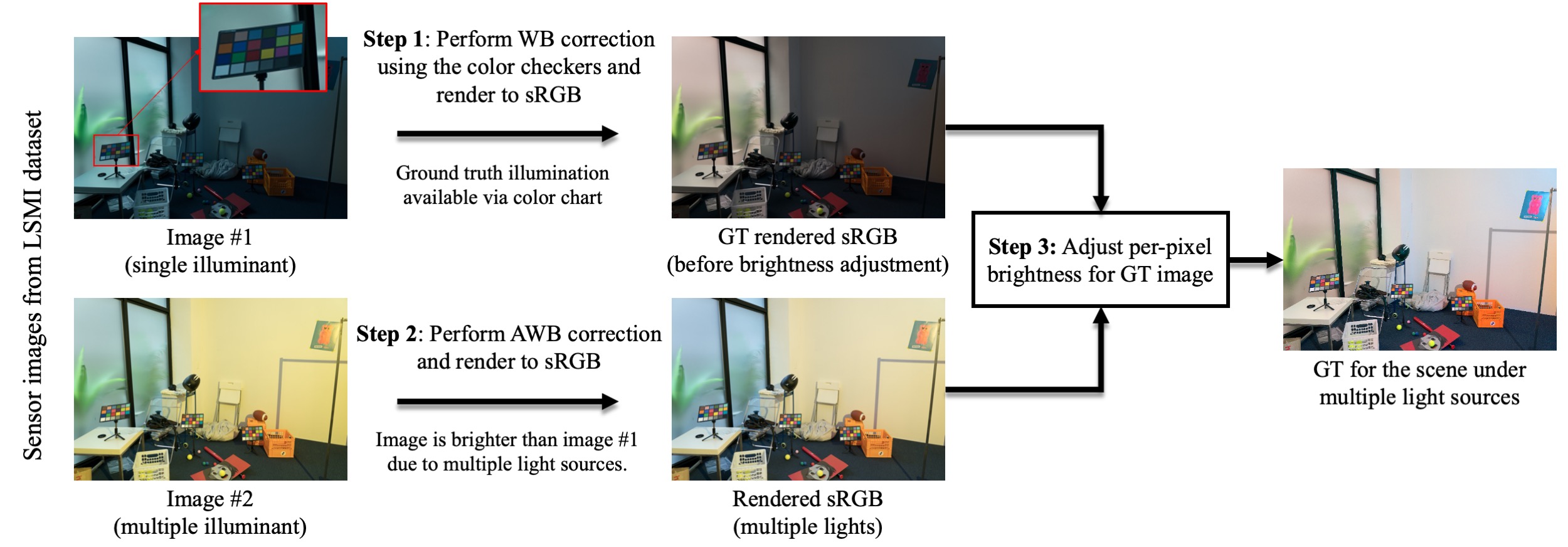
We repurpose the Sony and Nikon splits of the LSMI dataset. We render all the images with multiple illuminants into five different WB presets: Fluorescent (2850 Kelvin), Tungsten (3800 K), Daylight (5500 K), Cloudy (6500 K), and Shade (7500 K). To obtain the ground truth, we first apply WB correction using the color chart on the single illuminant image, as shown in step 1 of the Figure below. However, this initial ground truth image often has less brightness than an image of the same scene with additional light sources. To correct the brightness discrepancies, we render the multi-illuminant image to sRGB using a standard AWB procedure as shown in step 2 of the Figure below. While AWB does not produce a correct WB image under mixed lighting, it provides a reference for per-pixel brightness normalization of the single-illuminant ground truth image, as shown in step 3 of the Figure below. This brightness adjustment assumes a Lambertian reflectance model, a fair approximation for plausible white-balanced images that maintain spatial consistency with multi-illuminant images. Our dataset provides a valuable benchmark for training and evaluating fusion-based multi-illuminant WB methods, as it introduces real-world variations absent in the synthetic test set. The final dataset includes 16,284 sRGB images from the Nikon and Sony sets.
The dataset can be downloaded separately by:
Sony Split - 4K (Soon - We are figuring out how to store it.)
Nikon Split - 4K (Soon - We are figuring out how to store it.)
Citation
If you find this work useful for your research, please cite our paper:
@inproceedings{serrano2025revisiting,
author = {Serrano-Lozano, David and Arora, Aditya and Herranz, Luis and Derpanis, Konstantinos G. and Brown, Michael S. and Vazquez-Corral, Javier},
title = {Revisiting Image Fusion for Multi-Illuminant White-Balance Correction},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV)},
year = {2025},
pages = {8275-8284}
} Also, if you use our dataset, please cite the oriignal LSMI dataset:
@inproceedings{kim2021large,
title={Large scale multi-illuminant (lsmi) dataset for developing white balance algorithm under mixed illumination},
author={Kim, Dongyoung and Kim, Jinwoo and Nam, Seonghyeon and Lee, Dongwoo and Lee, Yeonkyung and Kang, Nahyup and Lee, Hyong-Euk and Yoo, ByungIn and Han, Jae-Joon and Kim, Seon Joo},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision},
pages={2410--2419},
year={2021}
} Acknowledgments
This work was partialy supported by grants PID2021-128178OB-I00, PID2024-162555OB-I00 funded by MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033 and by ERDF/EU, and by the Generalitat de Catalunya — Departament de Recerca i Universitats with reference 2021SGR01499 and CERCA Program. DSL also acknowledges the FPI grant from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (PRE2022-101525). LH was also supported by the Ramon y Cajal grant RYC2019-027020-I. This work was also partially supported by the grant C`atedra ENIA UAB-Cru ̈ılla (TSI-100929-2023-2) from the Ministry of Economic Affairs and Digital Transition of Spain. This work was funded in part by the CFREF (VISTA) program, an NSERC Discovery Grants, and the Canada Research Chair program.